Despite entering a period of recovery post-pandemic, the restaurant and hospitality industry is growing as it adapts to evolving consumer trends and a looming potential recession. At the forefront of this growth is QSR and fast casual franchises. Going into 2025, understanding the latest market trends is crucial for both new and seasoned franchisees with the rise of consumer preferences for convenience, affordability, and sustainability. Paperchase’s franchising experts dive into the market trends essential to success this year.
Economic Factors
In 2024, the state of the franchise industry in the United States is undergoing a period of growth as it adapts to a fluctuating economy. In the past year, the franchising sector in the US soared past 800,000 recorded franchise establishments, contributing to $850 billion annually. According to the International Franchise Association, this led to a 5% rise in sales from 2023, proving the industry as a competitive asset in the wake of an uncertain economic future. Within the $850B, QSRs (Quick Service Restaurants) are the dominating segment with over $250B in annual revenue and over 300,000 units, the IFA claims.
According to the National Restaurant Association, food costs have gone up 29% over the last 4 years due to inflation. Still, franchises, specifically QSR and fast casual restaurants have adapted to this fiscal slump. Buyers are drawn to QSR franchises because of their affordability and speed capability. With the “food away from home prices” ranking at 5.2% in 2024, there is no question why consumers are drawn to this segment of the franchise industry in the wake of financial uncertainty, as reported by the Consumer Price Index.
Looking ahead to 2025 proves promising for franchises despite overall negative fluctuations in the economy. While summer often produces low sales or general interest in franchising, this tide typically shifts in September and maintains momentum through November. Experts speculate that the Federal Reserve Board will lower interest rates going into Q4 2024, leading to higher demand for franchising towards the end of the year. These trends mirror that of 2022 to 2023 which saw a 5% increase in franchising. Analysts predict a strong Q1 for franchises in 2025 if these trends maintain their upward pull Within a rise in franchising at the end of 2024, the acquisitions of QSRs are increasing because of post- pandemic financial recovery married with siphoned demand and supply. According to PwC, around 60% of restaurant CEOs are expected to make at least one acquisition or plan for expansion going into 2025.
These M&As are largely influenced by inorganic growth because of the uncertainty around when the Federal Reserve will cut interest rates. Leading the pack are Burger King and Jersey Mikes, with BK boasting 4.6% sales growth in Q1 of 2024. This is largely in part due to a $300 million modernization project of Burger King franchises across the US, according to Restaurant Brands International.
Demographic and Consumer Trends
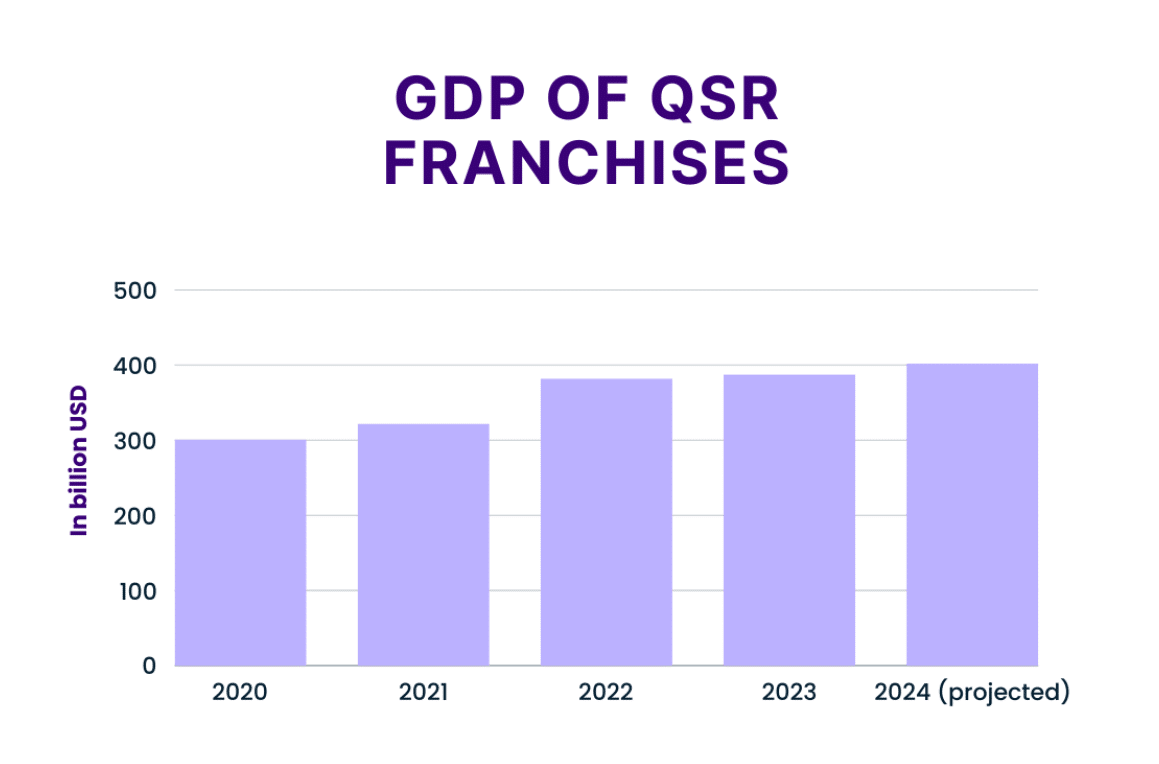
Fortune Business Insights claims that the GDP of QSR franchises will grow from $862.05 billion to $1,467.04 billion over the next five years. This is partially in part to a The demographic of franchise consumers has seen a change due to rapid urbanization and convenience. Market research shows that over 50% of consumers are drawn to franchises because of affordability, speed, and convenience. According to Nation’s Restaurant News, 60% of franchise consumers live in urban areas in 2024. A direct correlation to this upward trend in urban consumption is convenience. Franchises remain popular in areas with a large concentration of offices and commuters.
As the US slowly approaches a recession, consumers are spending less money on food at home and more at restaurants, specifically QSRs. Inflation has increased grocery prices across the country, leading many Americans to opt for the affordability of fast-casual restaurants. According to the US Department of Agriculture’s Economic Research Service, spending on food away from home has increased 13% since 2019, despite slight fluctuations during the pandemic. This same survey revealed that 6/10 American consumers preferred takeout or delivery when spending money on food away from home.
Even with changes in consumer habits forecasting increased traffic to fast-casual eateries, Americans struggle with credit card debt and loans. Younger consumers with more debt are drawn to spending money at fast casual and QSR establishments, especially with added incentives and loyalty programs. A rise in app-based restaurant loyalty programs has proved lucrative for fast casual franchises. Chipotle, for example, has capitalized on its loyalty program by offering 10 points for every dollar spent with additional free perks offered throughout the year. Operators can save money by implementing these programs without raising menu prices. Studies show that members of a loyalty program spend 5% more per visit than non-members. Additionally, the value of a loyal customer is higher, potentially increasing a restaurant’s profit margins by upwards of 25-100%.
Technological Advancements
Franchisors are positioned to experience exponential growth in 2025 as the role of technology becomes increasingly pertinent in this sector of the industry. One of the most impactful ways technologies are reshaping operations is through AI-powered systems that optimize everything from inventory management to staff scheduling. Automation has become a game-changer, with advanced point-of-sale systems, kiosks, and online ordering platforms minimizing human error and increasing efficiency during peak hours. Franchisors are prioritizing automation to save money on labor costs. This allows restaurants to handle a higher volume of orders with less staff, reducing operational costs and enhancing service speed. Although concerns over the loss of jobs around the implementation of AI are present in this sector, most of the automation present in the industry exists to ease the jobs of physical workers and promote accuracy.
For customers, these technological advancements translate into a more seamless and engaging experience. According to the National Restaurant Association, adult consumers are 30% more likely to use restaurant technology in 2024. Digital ordering through mobile apps or self-service kiosks has become standard, allowing customers to customize their meals, pay digitally, and provide an overall seamless experience. Integration of loyalty programs into these platforms further enhances the customer experience by offering tailored rewards and incentives. In addition, technologies like predictive analytics help franchises anticipate customer demand, allowing for better preparation during busy times and ensuring a consistently positive dining experience. Your Paperchase hospitality accountant can ensure that disparate revenue streams and ordering methods are accurately recorded and analyzed.
Franchise Industry Trends
While quick-service restaurants (QSR) and fast-casual eateries remain dominant, certain subcategories within these sectors see significant momentum. Fast casual chains like Chipotle and Shake Shack are capitalizing on the growing demand for healthier, more sustainable dining options. Meanwhile, virtual restaurants, like Ghost Kitchens, which focus on delivery-only models, are rapidly expanding in response to consumer preferences for convenience and the rise of online food delivery platforms as previously mentioned.
Companies like McDonald’s and Starbucks hold strong internationally, but the US appetite has shifted to newer establishments like Cava and Dave’s Hot Chicken, both of which had an extremely successful 2023, with signs pointing towards continued growth going into 2025. Franchisees are seeking to scale their portfolios by owning multiple units, especially in sectors like QSR. Companies like Burger King and Pizza Hut have successfully incentivized multi-unit franchisees, recognizing the financial benefit of multi-locations.
Global Franchise Industry
International expansion is also a key trend for the franchise industry in 2025, with brands looking to capitalize on emerging markets where consumer appetite for Western brands and dining experiences is growing. In Europe, Five Guys has seen growth at rates that rival its US counterparts. The burger joint has grown to over 250 locations across the UK, Germany, France, and Spain, a 14-unit increase from 2023. Despite inflation trends like that in the US, the GDP of Five Guys Europe rose 90 million euros between 2022-2023, proving the franchise’s global resilience.
Similarly, the hospitality industry in the Middle East has turned the tide towards franchises, specifically QSR and fast casual operations. Operating mostly out of the United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia, and Qatar, the Middle East franchise sector has a net worth of $33 billion. The United States has a strong hold on this facet of the industry with 71% of all Franchise brands in the region being American-made. The two biggest players in this field are McDonald’s, which makes up about 28% of all franchises in the Middle East, and Starbucks, which recently grew to over 400 units in Saudi Arabia alone.
Conclusion
The franchise industry in 2025 is navigating a dynamic landscape shaped by both external challenges and evolving consumer preferences. Despite potential economic uncertainties, the franchise sector continues to grow with subcategories like fast casual dining leading the charge. Technology, from AI-driven automation to digital ordering systems, is revolutionizing operations, improving efficiency, and enhancing the customer experience, all while expanding economic opportunities for franchisees. Despite an economy in flux and changing consumer preferences, franchises are in the perfect position to maintain their growth going forward into 2025. Paperchase’s hospitality experts can help you through any stage of the process. Whether you own 5 locations or 50, our CFO and advising team are franchise experts and can give operators the peace of mind they need to capitalize on industry trends and an evolving market.
Bibliography
Read more